Vehicle Thermal Management

Vehicle thermal management is gaining increased importance as more vehicle systems require cooling.
The challenge involves providing the optimum cooling, which meets the requirement with minimum power consumption, reduced frontal area to reduce aerodynamic drag, and a compact system with minimum weight.
Vehicle terminal management involves:
- Engine cooling
- Cabin Cooling /HVAC
- HV Battery cooling
- Power electronics cooling
- E-Machine Cooling
- Hydrogen fuel cell thermal management
Even though EV thermal management has gained more popularity recently, the underlying principles are similar to conventional cooling systems:
- Air cooled
- Liquid/coolant-cooled with the radiator
- Refrigerant cooling
The basic cooling system design includes matching the heat rejection to the system's cooling capacity in worst-case conditions.
Different development stages involve:
- 1D- Simulation
- Design
- 3D-Simulation
- Development test in worst-case conditions (RWUP)
For a conventional engine, the heat rejection capacity of the radiator should be equal to the sum of the heat rejection of the engine (typically 30% of total energy generated due to burning of fuel) plus heat rejection from other systems like (HVAC, Intercooler, etc).
For EV vehicle motor, power electrons and HV batter must be maintained at optimum temperature for best performance and durability.
HV battery cooling is very important in India's current scenario of fire incidents due to higher ambient conditions, harsh drive cycles, and usage profiles.
Major important are:
- Battery chemistry (NMC, LFP, etc)
- Cooling system design architecture and logic
- Production quality and consistency
Silicon thermal pads improve heat dissipation, provide good electrical insulation performance, vibration isolation, avoid friction and damage between the cells.
Hence pad between the tube and the battery avoids short circuits.
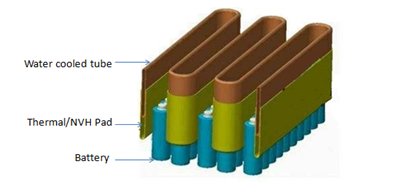
Battery Pack Cooling
The below layout shows a typical EV thermal management system in which a cooling loop cools the Motor, and power electronics and battery are cooled by another loop cooled by a heat exchanger (HX) cooled by an evaporator of a refrigerant loop.
Many possible layouts are used in EV thermal management layout.
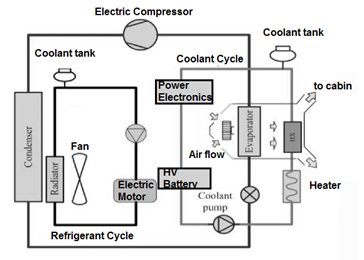
Typical Electric Vehicle Cooling System
This article was contributed by our expert Vibin Jacob
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
