Large Action Models: The Next AI Wave
Chat GPT changed the way humans interacted with machines. It also set the ball rolling for innovation in a completely new and unexplored territory of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Ever since, the artificial intelligence ecosystem has been evolving, with Large Action Models (LAMs) emerging as the next breakthrough and the paradigm of unexplored possibilities.
These AI- driven innovative models, LAMS, revolutionize how we interact with technology, bridging the gap between understanding human intentions and executing relevant actions. If the LLMs enable human-machine collaboration to ideate, the LAMs elevate this partnership to the next level of transforming thought into action.
In this article, we explore the evolution of LAMs, their working principles, potential use cases, and their impact on various sectors.
Evolution of Large Action Models
LAMs extend the capabilities of traditional Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating an action dimension into the already existing model. Unlike LLMs, which focus solely on understanding natural language, LAMs enhance the user experience by improving the human-machine collaboration. They complete the loop by enabling an action for the use request.
Rabit r1 is one such device that enables users to interact with the system and complete actions.
A typical LAM comprises natural language components and workflows to complete the action. The components of a LAM are as below:
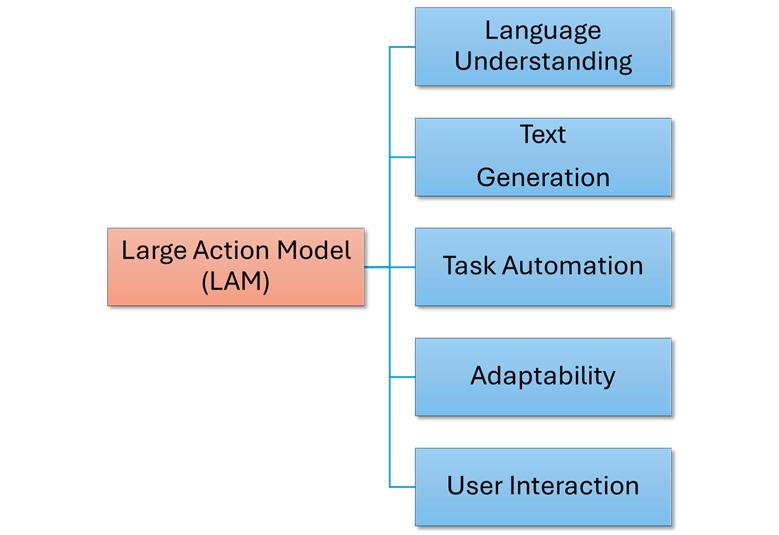
Figure1: Components of LAM
Language Understanding: LAMs can understand and interpret human language, including processing instructions, requests, and conversations.
Text Generation: They can generate text smoothly and naturally, enabling them to respond to queries, compose messages, and provide relevant information.
Automated Tasks: LAMs automate repetitive or complex tasks by integrating tools and data to accomplish specific goals.
Adaptability: These models adapt to changing circumstances by adjusting responses and actions based on context and new information.
User Interaction: LAMs interact with users, providing clear responses and soliciting feedback.
How Large Action Models Work
LAMs combine natural language understanding with actionable capabilities. When a user interacts with a LAM, the model processes the input, interprets the intent, and generates an appropriate response. Under the hood, LAMs leverage neural architectures, large-scale pre-training, and fine-tuning on specific tasks.
Integrated workflows enable LAMs to complete actions accurately and swiftly. They learn from vast amounts of data, enabling them to perform tasks efficiently and accurately.
Possible Use Cases of LAMS
The impact of LAMs is evident across various domains. Let's consider a possible use case:
Healthcare Strategies
Patient Care Transformation: LAMs can enhance patient care through modern diagnostics and personalized treatment strategies.
Disease Diagnosis and Monitoring: They can assist in diagnosing diseases and monitoring patient health.
Treatment Recommendations: LAMs can recommend tailored treatment options based on patient data.
Financial Technology (FinTech)
Risk Measurement: LAMs can help analyze risks associated with financial transactions.
Fraud Detection Systems: They can identify fraudulent activities by analyzing patterns and anomalies.
Algorithmic Transactions: LAMs can automate algorithm-based financial transactions.
Automotive Industry
Self-Driving Cars: LAMs can contribute to improving self-driving vehicles by making real-time decisions based on sensor data.
Vehicle Safety Systems: They can enhance vehicle safety features by predicting and preventing accidents.
Consumer Electronics
Personalized User Experiences: LAMs can create personalized experiences in devices such as robotics, smart home assistants, and wearable technology.
Robotics and Automation
Human-Robot Interaction: LAMs can enhance automation and improve communication between humans and robots.
Conclusion
Large Action Models (LAMs) represent a new era in human-machine collaboration. As these models continue to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enhancing user interactions. Thanks to LAMs, the journey from understanding language to executing meaningful actions is now more seamless than ever.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main challenges in scaling LAMs for real-world applications?
While LAMs are the next paradigm for AI, the road to real-world acceptance is still faced with challenges. The prominent ones are:
Ethics and Responsible AI
AI models typically amplify bias and discrimination if not implemented with the right guardrails. Since LAMs also trigger actions based on the comprehension of the underlying model, it becomes essential to ensure the ecosystem is evaluated and implemented responsibly to ensure fair and non-discriminative actions.
Data and Integration
Data is a key component in training a model. The better the data, the better the actions and outcomes of the models. Ensuring the right data is integrated accurately can drastically improve the performance of the large action models.
Reliability and Transparency
Understanding how LAMs arrive at certain conclusions is essential to ensuring reliability and trust in the models' outcomes. Building mechanisms to explain the outcomes of large action models is a must before developing real-world applications.
2. What new market opportunities are emerging due to advancements in LAMs and AGI?
Grid Management
Large Action Models can forecast energy demand and thus facilitate grid management. The outcome of actions can help improve meeting energy consumption demands.
Production Management
LAMs enable continuous monitoring of sensor data from machines, including data from other sources. The model can then analyze the data and take appropriate action to ensure optimum production levels.
Smart Supply Chain
LAMs can help optimize supply chains by suggesting vendors, best routes and order delivery.
3. What are the current trends in investment in LAMs and AGI research and development?
Enterprises and Hyperscalers
LAMs have gained a lot of popularity as the next big thing in Artificial General Intelligence. Microsoft and Salesforce have systematically been investing in developing LAMs. Apple has been upgrading Siri to take specific actions rather than just provide answers.
Governments
Governments have been investing heavily in AI and primarily in large action models to enable digital governance initiatives. Artificial General Intelligence and Generative AI can play a crucial role to enable ease of accessing resources for citizens.
4. What are the key market trends to watch in the next 5-10 years regarding LAMs and AGI?
Ethical AI
While AI and LAMs, in particular, can transform organizations, there are still issues and questions around the ethical use of AI. If LAMs are not trained to decide which decisions are ethical, the consequences could be disastrous. The next few years will see AI providers and developers striving to ensure the use of AI stays ethical and the actions stay within the guardrails provided.
Quantum AI
Quantum computing can provide the much-needed computing power to run large-scale Generative AI models. With quantum computing ecosystems, LAMs can be trained more efficiently to drive relevant actions on an enterprise scale. Though the world is still waking up to quantum computing, the next decade will see profound interest in developing next-generation computing power.
Human-machine collaboration
Though LAMs try to mimic the human brain for driving actions, they are still in the neo-nascent stage. It is essential that LAMs work with Humans to augment decision-making rather than being individualistic. The next few years will see multiple new interfaces evolve to enable these collaborative actions.
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
